- Le Pôle
- Programmes
- Entreprises
- Research Center
- International
- Vie étudiante
- Presse
- Agenda
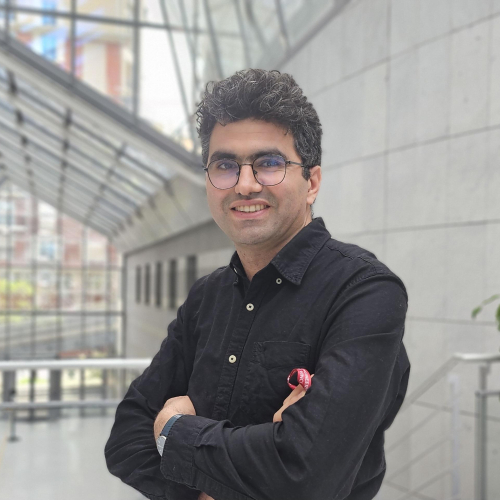

Saad Benjelloun graduated from Ecole Nationale Supérieure des Techniques Avancées (Paris) in 2009, then he followed a PhD program in Ecole Normale Supérieure of Saclay (ex- ENS-Cachan), defending his PhD thesis in 2012. He also got a Habilitation to Direct the Research (HDR) from the University Mohammed VI Polytechnique, Morocco, in 2023. Before joining the ESILV, he has worked as a permanent researcher at Total-Energies R&D center (2 years) in Pau, France, University Mohammed VI Polytechnique in Benguerir, Morocco (8 years), and as scientific director of Makhbar Research Center in Casablanca, Morocco (1 year). His main research interests include the theoretical investigation of multiphase fluid models, the modeling and simulation of complex industrial chemical process, as well as the mathematical foundations of Artificial Inteligence.
Mohamed Amine Ouchdiri; SAAD BENJELLOUN; Adnane Saoud; Irene Otero-Muras
Turing patterns in a morphogenetic model with single regulatory function Article de journal
Dans: Mathematical Biosciences, vol. 389, p. 109536, 2025.
@article{ouchdiri_3897,
title = {Turing patterns in a morphogenetic model with single regulatory function},
author = {Mohamed Amine Ouchdiri and SAAD BENJELLOUN and Adnane Saoud and Irene Otero-Muras},
url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.mbs.2025.109536},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-11-01},
journal = {Mathematical Biosciences},
volume = {389},
pages = {109536},
abstract = {Confirming Turing's theory of morphogens in developmental processes is challenging, and synthetic biology has opened new
avenues for testing Turing's predictions. Synthetic mammalian pattern formation has been recently achieved through a reaction-
diffusion system based on the short-range activator (Nodal) and the long-range inhibitor (Lefty) topology, where a single function
regulates both morphogens. In this paper, we investigate the emergence of Turing patterns in the synthetic Nodal-Lefty system.
First, we prove the existence of a global solution and derive conditions for Turing instability through linear stability analysis.
Subsequently, we examine the behavior of the system near the bifurcation threshold, employing weakly nonlinear analysis, and
using multiple time scales, we derive the amplitude equations for supercritical and subcritical cases. The results demonstrate the
ability of the system to support various patterns, with the subcritical Turing instability playing a crucial role in the formation of
dissipative structures observed experimentally.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
SAAD BENJELLOUN; Salma Lahbabi; Abdelqoddous Moussa
Homogenization of two-dimentional materials in the Thomas-Fermi-von Weizsäcker theory Article de journal
Dans: Journal Of Mathematical Physics, vol. 66, no. 7, p. 072106, 2025.
@article{benjelloun_3848,
title = {Homogenization of two-dimentional materials in the Thomas-Fermi-von Weizsäcker theory},
author = {SAAD BENJELLOUN and Salma Lahbabi and Abdelqoddous Moussa},
url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/5.0191472},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-07-01},
journal = {Journal Of Mathematical Physics},
volume = {66},
number = {7},
pages = {072106},
abstract = {We study the homogenization of the Thomas-Fermi-von Weizsäcker (TFW) model for two-dimentional (2D) materials introduced in [Blanc and Le Bris, Adv. Differ. Equations 5, 977-1032 (2000)]. It consists in considering 2D-periodic nuclear densities with periods going to zero. We study the behavior of the corresponding ground state electronic densities and ground state energies. The main result is that these three-dimensional problems converge to a limit model that is one dimensional, similar to the one proposed in [Gontier et al., Commun. Math. Phys. 388, 1475-1505 (2021)]. We also illustrate this convergence with numerical simulations and estimate the converging rate for the ground state electronic densities and the ground state energies.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Ahmed Ja; SAAD BENJELLOUN; Jean Michel Ghidaglia; Faical Ait Lahbib
Dynamic fluid flow model for phosphate slurry pipeline: OCP main pipeline as case study Article de journal
Dans: International Journal Of Multiphase Flow, vol. 181, p. 105011, 2024.
@article{ja_3172,
title = {Dynamic fluid flow model for phosphate slurry pipeline: OCP main pipeline as case study},
author = {Ahmed Ja and SAAD BENJELLOUN and Jean Michel Ghidaglia and Faical Ait Lahbib},
url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S030193222400288X},
year = {2024},
date = {2024-12-01},
journal = {International Journal Of Multiphase Flow},
volume = {181},
pages = {105011},
abstract = {The transportation of phosphate slurry through large-scale pipelines presents significant challenges due to the complex behavior of multiphase flows, particularly with varying solid content, density, and dynamic viscosity. Efficient and accurate prediction of flow behavior is critical for optimizing the operation of such pipelines. This work aims to develop a dynamic computational model to simulate phosphate slurry flow in pipelines. The case study focuses on the OCP Group's main slurry pipeline, which links the mining sites at Khouribga to the industrial plants at Jorf Lasfar, Morocco. This pipeline system spans a total length of 187.124 km, consisting of 5237 pipes with an inner diameter ranging from 0.8546 m to 0.8578 m, and features several elevation changes along its ground level. Using a section-averaged, dynamic approach and the Finite Volume scheme, the model computes essential flow parameters, including density, dynamic viscosity, and pressure, for the incompressible and non-Newtonian slurry and process water flows. The model's accuracy is validated against on-site measured data, showing an average deviation of ±0.32% for outlet density, and below 10% for pressure along the pipeline, underscoring the model's reliability. Additionally, a sensitivity analysis was conducted to illustrate the impact of key parameters on the predicted head losses and pressures along the pipeline. This analysis shows that the slurry viscosity is the most critical parameter, significantly influencing these predictions. This model provides high accuracy and reasonable CPU time for real-time simulation and monitoring, while also offering significant potential for optimizing pipeline operations and ensuring the reliability of phosphate transport.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Azeddine Zaidni; Philip J. Morrison b; SAAD BENJELLOUN
Thermodynamically consistent Cahn-Hilliard-Navier-Stokes equations using the metriplectic dynamics formalism Article de journal
Dans: Physica D-Nonlinear Phenomena, vol. 468, p. 134303, 2024.
@article{zaidni_3133,
title = {Thermodynamically consistent Cahn-Hilliard-Navier-Stokes equations using the metriplectic dynamics formalism},
author = {Azeddine Zaidni and Philip J. Morrison b and SAAD BENJELLOUN},
url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0167278924002549},
year = {2024},
date = {2024-11-01},
journal = {Physica D-Nonlinear Phenomena},
volume = {468},
pages = {134303},
abstract = {Cahn-Hilliard-Navier-Stokes (CHNS) systems describe flows with two-phases, e.g., a liquid with bubbles. Obtaining constitutive relations for general dissipative processes for such systems, which are thermodynamically consistent, can be a challenge. We show how the metriplectic 4-bracket formalism (Morrison and Updike, 2024) achieves this in a straightforward, in fact algorithmic, manner. First, from the noncanonical Hamiltonian formulation for the ideal part of a CHNS system we obtain an appropriate Casimir to serve as the entropy in the metriplectic formalism that describes the dissipation (e.g. viscosity, heat conductivity and diffusion effects). General thermodynamics with the concentration variable and its thermodynamics conjugate, the chemical potential, are included. Having expressions for the Hamiltonian (energy), entropy, and Poisson bracket, we describe a procedure for obtaining a metriplectic 4-bracket that describes thermodynamically consistent dissipative effects. The 4-bracket formalism leads naturally to a general CHNS system that allows for anisotropic surface energy effects. This general CHNS system reduces to cases in the literature, to which we can compare.},
note = {soumis février 2024},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Ayoub Arraji; SAAD BENJELLOUN; Salma Lahbabi
Stability of the one electron atom Schrödinger model with magnetic field in two dimensions Article de journal
Dans: Advances In Theoretical And Mathematical Physics, vol. 28, no. 5, p. 1597-1623, 2024.
@article{arraji_3270,
title = {Stability of the one electron atom Schrödinger model with magnetic field in two dimensions},
author = {Ayoub Arraji and SAAD BENJELLOUN and Salma Lahbabi},
url = {https://link.intlpress.com/JDetail/1851628428481605634},
year = {2024},
date = {2024-10-01},
journal = {Advances In Theoretical And Mathematical Physics},
volume = {28},
number = {5},
pages = {1597-1623},
abstract = {We study the stability of the one electron atom Schrödinger model with self-generated magnetic field in two dimensions. The magnetic energy is taken of a general form and we study the stability of the model as a function of the power p and the coupling
constant K. We show that for p > 3/2, the model is always stable, and for p < 3/2, the model is always unstable. In the critical case
p = 3/2, there is a critical stability constant Kc, that we characterize in terms of zero modes of the Dirac-Weyl operator. The value
of Kc is approximated using analytic and numerical methods.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Abdelhak Elidrissi; Salem Nafiri; SAAD BENJELLOUN; Abdelhakim Khatab
Machine Learning-Based Approach to Predict Remaining Useful Life of Rolling Bearings: OCP as case study Proceedings Article
Dans: 2025 5th International Conference on Innovative Research in Applied Science, Engineering and Technology (IRASET), p. 1-6, Fez, Morocco, 2025, ISBN: 979-8-3315-3298-7.
@inproceedings{elidrissi_3699,
title = {Machine Learning-Based Approach to Predict Remaining Useful Life of Rolling Bearings: OCP as case study},
author = {Abdelhak Elidrissi and Salem Nafiri and SAAD BENJELLOUN and Abdelhakim Khatab},
url = {https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/11008037},
issn = {979-8-3315-3298-7},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-05-01},
booktitle = {2025 5th International Conference on Innovative Research in Applied Science, Engineering and Technology (IRASET)},
pages = {1-6},
address = {Fez, Morocco},
abstract = {Predictive maintenance is essential for minimizing downtime and optimizing the performance of critical industrial systems. In this study, we propose a machine learning-based approach to predict the Remaining Useful Life (RUL) of rolling bearings, a critical component in phosphate grinding mills. Unlike traditional methods that rely on vibration data, our approach leverages operational data, including shift of work, phosphate layer, phosphate quality, working time, tonnage of rock and cumulative metrics. Two predictive models were developed: Multiple Linear Regression (MLR) and Artificial Neural Networks (ANN). Experimental results demonstrate the potential of ANN-based model to enable precise RUL predictions, facilitating proactive maintenance scheduling and reducing unplanned downtime. The proposed approach is cost-effective, utilizes existing historical data, and can be extended to other industrial equipment and defect types.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
SAAD BENJELLOUN
The Conversation, 2025.
@misc{benjelloun_3949,
title = {Maths au quodidien : Full HD, 4K, 8K... ou pourquoi il n'est pas toujours utile d'augmenter la résolution de sa télévision},
author = {SAAD BENJELLOUN},
url = {https://doi.org/10.64628/AAK.ymc4vqqf4},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-10-01},
howpublished = {The Conversation},
note = {https://doi.org/10.64628/AAK.ymc4vqqf4},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {misc}
}
No posts by this author.
N'hésitez pas à contacter le service des admissions pour tout renseignement complémentaire :








